Python Dictionary
Dictionary in Python is a collection of keys values, used to store data values like a map, which, unlike other data types which hold only a single value as an element.
Example of Dictionary in Python
Dictionary holds key:value pair. Key-Value is provided in the dictionary to make it more optimized.
- Python3
Output:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}Creating a Dictionary
In Python, a dictionary can be created by placing a sequence of elements within curly {} braces, separated by ‘comma’. Dictionary holds pairs of values, one being the Key and the other corresponding pair element being its Key:value. Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be duplicated, whereas keys can’t be repeated and must be immutable.
Note – Dictionary keys are case sensitive, the same name but different cases of Key will be treated distinctly.
- Python3
Output:
Dictionary with the use of Integer Keys: {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} Dictionary with the use of Mixed Keys: {'Name': 'Geeks', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}Dictionary can also be created by the built-in function dict(). An empty dictionary can be created by just placing to curly braces{}.
Output:
Empty Dictionary: {} Dictionary with the use of dict(): {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} Dictionary with each item as a pair: {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For'}Complexities for Creating a Dictionary:
Time complexity: O(len(dict))
Space complexity: O(n)
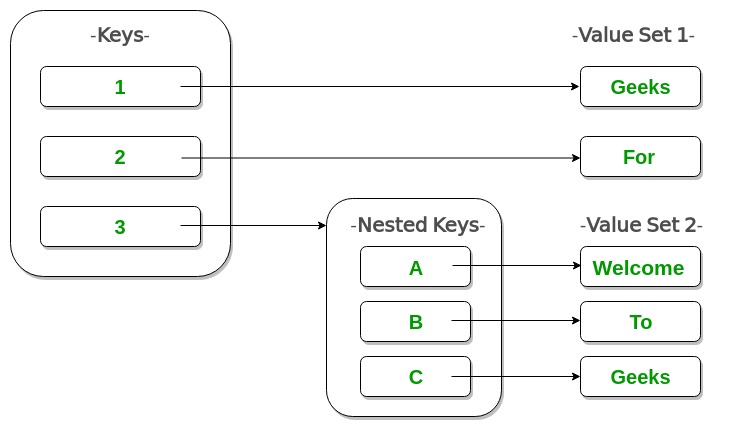
Nested Dictionary
- Python3
Output:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}Adding elements to a Dictionary
Addition of elements can be done in multiple ways. One value at a time can be added to a Dictionary by defining value along with the key e.g. Dict[Key] = ‘Value’. Updating an existing value in a Dictionary can be done by using the built-in update() method. Nested key values can also be added to an existing Dictionary.
Note- While adding a value, if the key-value already exists, the value gets updated otherwise a new Key with the value is added to the Dictionary.
- Python3
Output:
Empty Dictionary: {} Dictionary after adding 3 elements: {0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1} Dictionary after adding 3 elements: {0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)} Updated key value: {0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)} Adding a Nested Key: {0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4), 5: {'Nested': {'1': 'Life', '2': 'Geeks'}}}Complexities for Adding elements in a Dictionary:
Time complexity: O(1)/O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
Accessing elements of a Dictionary
In order to access the items of a dictionary refer to its key name. Key can be used inside square brackets.
- Python3
Output:
Accessing a element using key: For Accessing a element using key: GeeksThere is also a method called get() that will also help in accessing the element from a dictionary.This method accepts key as argument and returns the value.
Complexities for Accessing elements in a Dictionary:
Time complexity: O(1)
Space complexity: O(1)
- Python3
Output:
Accessing a element using get: GeeksAccessing an element of a nested dictionary
In order to access the value of any key in the nested dictionary, use indexing [] syntax.
- Python3
Output:
{1: 'Geeks'} Geeks For